写在前面
寒假也快过去了,给自己的任务还算是完成了,因为之前有算法和数据结构的基础,数据结构对于我来说压力并不大吧,这个博客用来总结这段时间对于数据结构的学习。
线性表
一共9个操作:
- InitList(&L);//初始化表
- Length()
- int locateElem/(sqList L, int e/);//按值查找
- int getElem/(sqList L, int i/);//按位置查找
- int listInsert/(sqList&L, int i, int e);//在第i个位置插入e
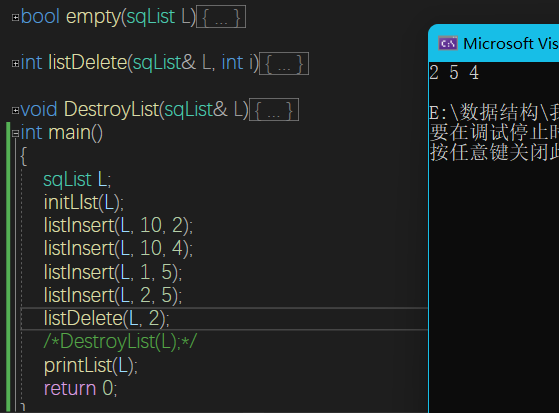
- int listDelete(sqList& L, int i);//
- void printList(sqList L);
- bool empty(sqList L);
- void DestroyList(sqList& L);//改变表的操作传入引用
顺序表

插入和删除操作需要移动大量元素,但查找效率很高
最大的特点是:随机访问,直接找到指定的元素,存储密度高
void initLIst(sqList& L)
{
L.length = 0;
}
int getLength(sqList L)
{
return L.length;
}
int locateElem(sqList L, int e) {
int loc = 0;
if (L.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
else {
while (L.data[loc] != e) {
loc++;
}
}
return loc;
}
int getElem(sqList L, int i) {
if (empty(L))return 0;
else if (i > L.length)return -1;
else return L.data[i];
}
int listInsert(sqList& L, int i, int e)
{
if (L.length + 1 > Max || L.length > Max) {
return 0;
}
else if (L.length == 0) {
L.data[0] = e;
L.length++;
return 1;
}
else if (i > L.length) {
L.data[L.length++] = e;
return L.length;
}
else {
for (int ind =L.length; ind > i; ind--) {
L.data[ind] = L.data[ind-1];
}
L.data[i] = e;
L.length++;
return L.length;
}
}
void printList(sqList L) {
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++) {
cout << L.data[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool empty(sqList L) {
if (L.length == 0)return true;
return false;
}
int listDelete(sqList& L, int i) {
if (empty(L))return 0;
else {
int e = L.data[i];
for (int ind = i; ind < L.length; ind++) {
L.data[ind] = L.data[ind + 1];
}
L.length--;
return e;
}
}
void DestroyList(sqList& L) {
memset(L.data, 0, sizeof(L.data) / sizeof(int));
L.length = 0;
}单链表
单链表引入了头结点,这使得在头部的插入操作变得极其简单
查找操作的时间复杂度为O(n)
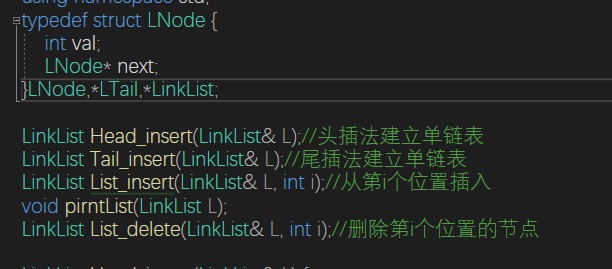
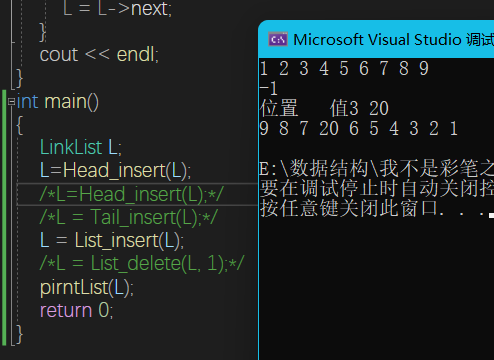
LinkList Head_insert(LinkList& L) {
LNode *newNode; int curVal=0;
L = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(newNode) );
L->next = NULL;
cin >> curVal;
while (curVal >= 0) {
newNode = (LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
newNode->val = curVal;
newNode->next = L->next;
L->next = newNode;
cin >> curVal;
}
return L;
}
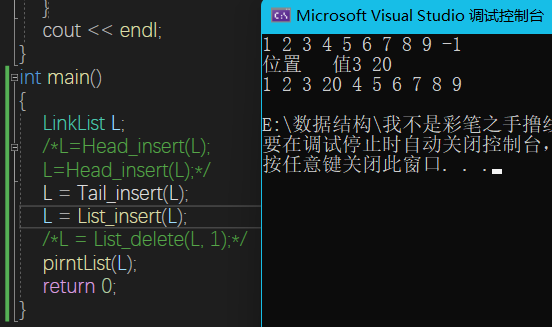
LinkList Tail_insert(LinkList& L) {
L = (LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
LNode *newNode,*r=L; int curval;
cin >> curval;
while (curval >= 0) {
newNode = (LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->val = curval;
r->next = newNode;
r = newNode;
cin >> curval;
}
r->next = NULL;
return L;
}
LNode* GetElem(LinkList& L, int i) {
LNode* temp = L->next;
int ind = 0;
while (ind != i) {
temp = temp->next;
ind++;
}
return temp;
}
LinkList List_insert(LinkList& L) {
int i, curval;
cout << "位置 " << "值";
cin >>i>> curval;
LNode* temp = GetElem(L, i - 1);
LNode* p,*q;
p = (LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
p->val = curval;
q = temp->next;
temp->next = p;
p->next = q;
return L;
}
LinkList List_delete(LinkList& L, int i)
{
LNode* temp =GetElem(L,i-1);
LNode* q = temp->next;
temp->next = q->next;
free(q);
return L;
}双链表
引入了前驱节点,使得可以逆转输出整个链表
并且删除操作可以直接找到前驱节点,操作的时间复杂度和单链表一样
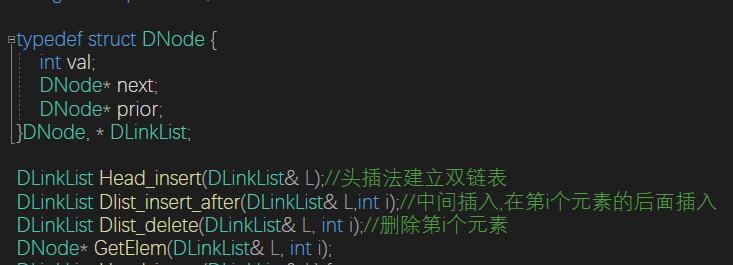
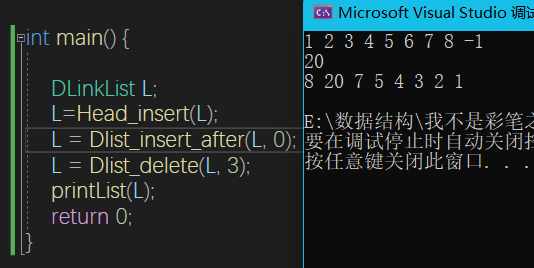
DLinkList Head_insert(DLinkList& L) {
DNode* newNode; int curVal = 0;
L = (DLinkList)malloc(sizeof(newNode));
L->next = NULL;
cin >> curVal;
while (curVal >= 0) {
DNode* pre = L;
newNode = (DNode*)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
newNode->val = curVal;
newNode->next = L->next;
newNode->prior = pre;
if(L->next!=NULL)
L->next->prior = newNode;
L->next = newNode;
cin >> curVal;
}
return L;
}
DLinkList Dlist_delete(DLinkList& L, int i) {
DNode* p = GetElem(L, i);
DNode* q = p->prior;
p->next->prior = q;
q->next = p->next;
free(p);
return L;
}
DLinkList Dlist_insert_after(DLinkList& L, int i) {
DNode* p = GetElem(L,i);
DNode* newNode;
newNode = (DNode*)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
int curval; cin >> curval;
newNode->val = curval;
DNode *q = p->next;
newNode->next = q;
p->next = newNode;
newNode->prior = p;
q->prior = newNode;
return L;
}
DNode* GetElem(DLinkList& L,int i) {
DNode* temp = L->next;
int ind = 0;
while (ind != i) {
temp = temp->next;
ind++;
}
return temp;
}
void printList(DLinkList L)
{
while (L->next != NULL) {
DNode* cur = L->next;
cout << cur->val << " ";
L = L->next;
}
cout << endl;
}循环链表
循环链表的最后一个节点的next节点指向头节点的next(头节点不存储)
所以判空条件变成最后一个节点是否是头节点,判满的条件是尾节点的next为头节点
对表头和表尾的操作都是O(1)
最好是用尾插法建立循环链表
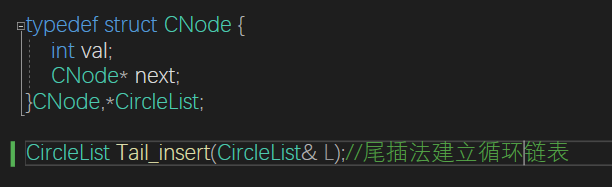
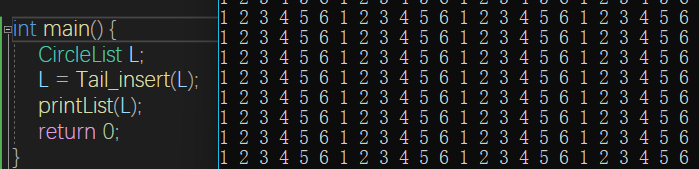
CircleList Tail_insert(CircleList& L) {
CNode* newNode,*r; int curval;
L = (CircleList)malloc(sizeof(CNode));
r = L;
r->next = NULL;
cin >> curval;
while (curval >= 0) {
newNode = (CNode*)malloc(sizeof(CNode));
newNode->val = curval;
r->next = newNode;
newNode->next = L->next;
r = r->next;
cin >> curval;
}
return L;
}
void printList(CircleList L,int t)
{
while (L->next != NULL&&t!=0) {
CNode* cur = L->next;
cout << cur->val << " ";
L = L->next;
t--;
}
cout << endl;
}
void printList(CircleList L)
{
while (L->next != NULL) {
CNode* cur = L->next;
cout << cur->val << " ";
L = L->next;
}
cout << endl;
}线性表总结:
- 顺序表可以随机存储,链表只能从表头顺序读取元素
- 顺序存储的数据物理位置也相邻,链式存储相邻元素物理位置不一定相邻
- 对于按值查找顺序表和链表都是O(n),按位置查找顺序表是O(1)
- 顺序表一旦容量满则不能扩容,链表可以动态增加存储空间
栈,队列,数组
顺序栈
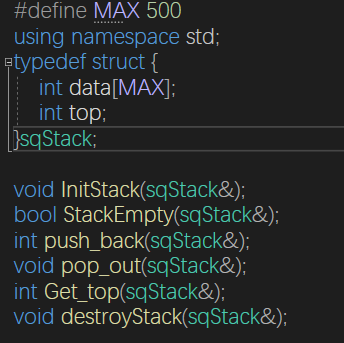
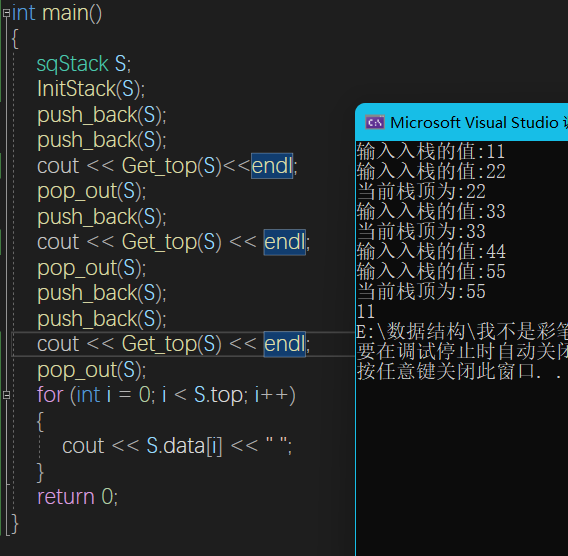
void InitStack(sqStack &S) {
memset(S.data, 0, MAX*sizeof(int));
S.top = -1;
}
bool StackEmpty(sqStack& S) {
if (S.top <= -1)return true;
return false;
}
int push_back(sqStack& S) {
int val;
cin >> val;
S.data[++S.top] = val;
return val;
}
void pop_out(sqStack& S) {
S.top--;
}
int Get_top(sqStack& S) {
return S.data[S.top];
}
void destroyStack(sqStack& S) {
free(S.data);
S.top = -1;
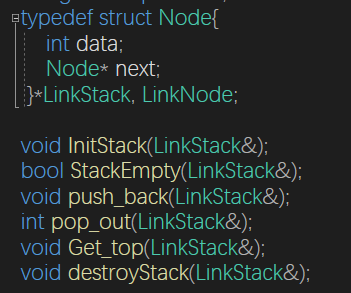
}链栈
void InitStack(LinkStack& top)
{
top->next = NULL;
}
bool StackEmpty(LinkStack& top) {
if (top->next == NULL)return true;
return false;
}
void push_back(LinkStack& top)
{
int curval; cin >> curval;
top = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(LinkNode));
LinkNode *newnode;
newnode = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(LinkStack));
newnode->data = curval;
newnode->next = NULL;
top->next = newnode;
}
int pop_out(LinkStack& top) {
if (StackEmpty(top))return 0;
else {
LinkNode* temp = top->next;
top->next = temp;
/*free(temp);
temp->next = NULL;*/
return true;
}
}
void Get_top(LinkStack& top)
{
if (StackEmpty(top))cout << "空栈";
else
{
if (top->next != NULL) {
cout << top->next->data;
}
}
}
采用链式存储,便于节点的插入与删除,入栈和出栈的操作都在链表表头进行,需要注意的是,对于带表头的和不带表头的链栈,具体实现方法会不同
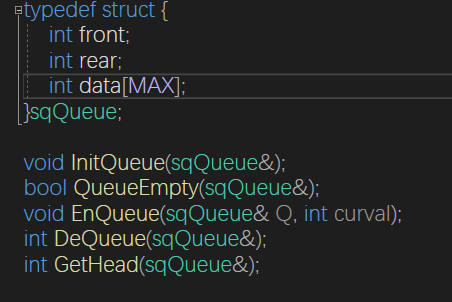
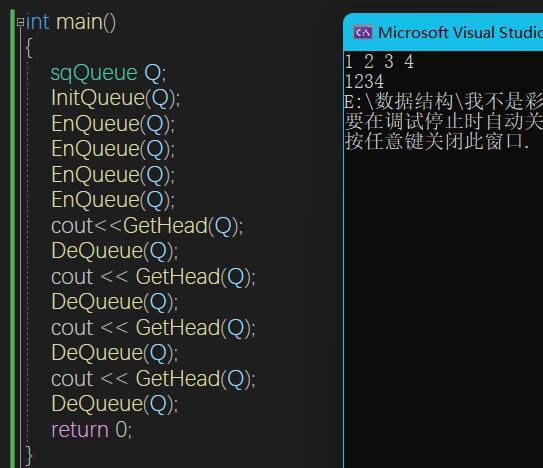
顺序队列
void InitQueue(sqQueue& Q) {
memset(Q.data, 0, sizeof(Q.data));
Q.front = 0;
Q.rear = 0;
}
bool QueueEmpty(sqQueue& Q) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear)return true;
return false;
}
void EnQueue(sqQueue& Q, int curval) {
Q.data[Q.rear++] = curval;
}
int DeQueue(sqQueue& Q) {
if (QueueEmpty(Q))return false;
Q.data[Q.front++];
return true;
}
int GetHead(sqQueue& Q) {
return Q.data[Q.front];
}
- 初始状态:front==rear==0
- 队满状态:rear-front==MAXSIZE
- 队空状态:rear==front
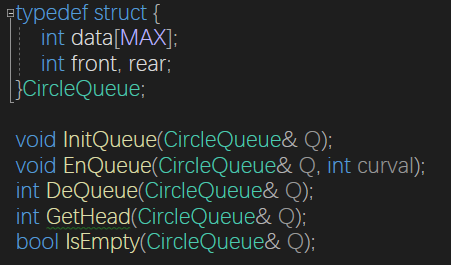
循环队列
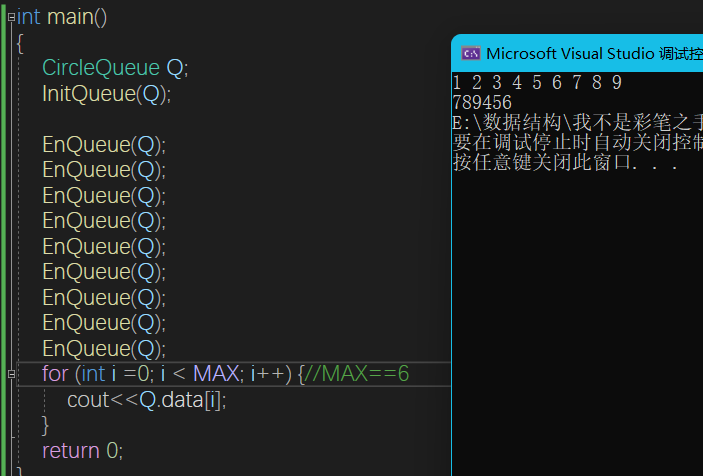
void InitQueue(CircleQueue& Q) {
Q.front = Q.rear = 0;
memset(Q.data, 0, sizeof(Q.data)/sizeof(int));
}
void EnQueue(CircleQueue& Q, int curval=0) {
cin >> curval;
if (Q.rear + 1 % MAX == Q.front % MAX)//rear在front前面说明队满
{
DeQueue(Q);
Q.data[(Q.rear++)%MAX] = curval;
}
else {
Q.data[(Q.rear++) % MAX] = curval;
}
}
int DeQueue(CircleQueue& Q) {
if (IsEmpty(Q))return 0;
else {
Q.front++;
return 1;
}
}
bool IsEmpty(CircleQueue& Q) {
if (Q.rear%MAX == Q.front % MAX)
return true;
return false;
}- 初始状态:rear==front==0
- 队满状态:(rear+1)%MAXSIZE==front//rear在front前面一个
- 队空状态:rear==front
- 队中元素个数(rear-front+Maxsize)%Maxsize
链队
void InitQueue(LinkQueue& Q) {
Q.front = Q.rear = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Q.front->next = NULL;
}
void EnQueue(LinkQueue& Q, int curval=0) {
cin >> curval;
Node* newnode;
newnode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
newnode->data = curval;
newnode->next = NULL;
Q.rear->next = newnode;
Q.rear = Q.rear->next;
}
int DeQueue(LinkQueue& Q) {
if (IsEmpty(Q))return 0;
else {
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp = Q.front;
Q.front = Q.front->next;
if (Q.rear == temp)//如果只剩一个元素删完则队列置空
Q.front = Q.rear;
free(temp);
return 1;
}
}
int GetHead(LinkQueue& Q) {
return Q.front->next->data;
}
bool IsEmpty(LinkQueue& Q) {
if (Q.front == Q.rear)return true;
return false;
}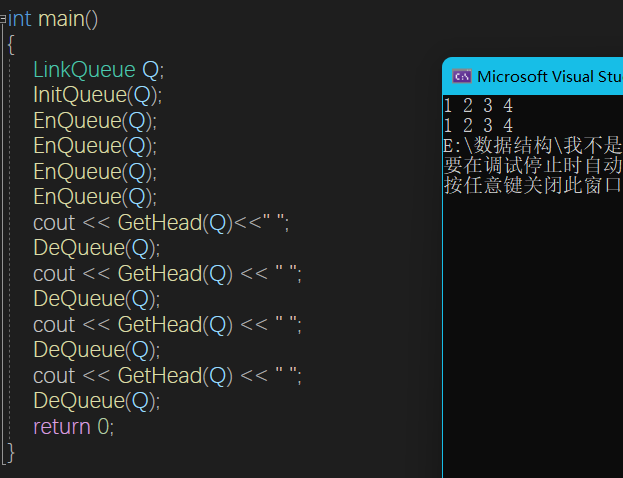
用单链表表示的链式队列特别适合于树据元素变动比较大的情形,而且不存在队满且产生溢出的情况
括号匹配(栈的应用)
bool is(string ss) {
stack<char> ops;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length(); i++) {
if (ss[i] == '(')ops.push(ss[i]);
if (ss[i] == ')') {
if (ops.empty())
{
return 0;
}
else ops.pop();
}
}
if (ops.empty())return 1;
return 0;
}中缀表达式转后缀表达式
王道P98-p99
队列的作用
- BFS
- FIFO
串
KMP算法
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string s, ss;//s主串,ss模式串
int next1[105];//next数组
void getnext()
{
next1[1] = 0;
int i = 1, j = 0;//i=j+1
while (i != ss.length()-1) {
if (j == 0 || ss[i] == ss[j]) {//第一个字母的next为1
//i表示当前在比较模式穿中前i个字符的最长公共字串
//j表示当前公共字串长度
next1[++i] = ++j;//当前第i个字符前的最长公共串长度
}
else {
j = next1[j];//如果发生失配就往前面找,直到j=0使得next[j]=1
}
}
}
int index_KMP() {
int i = 1, j = 1;//主串和模式串同时向前推动,发生失配模式串向前走
while (i <= s.length()-1 && j <= ss.length()-1) {
if (j == 0 || s[i] == ss[j]) {
++i; ++j;
}
else {
j = next1[j];
}
}
if (j > ss.length()-1)return i - ss.length()+1;//主串跑完了,模式串还没有匹配则return0
else return 0;
}
int main(void) {
getline(cin, s);
/*cout << s.length();*/
getline(cin, ss);
s.insert(s.begin(), ' ');
ss.insert(ss.begin(), ' ');
getnext();
cout << index_KMP();
return 0;
}树与二叉树
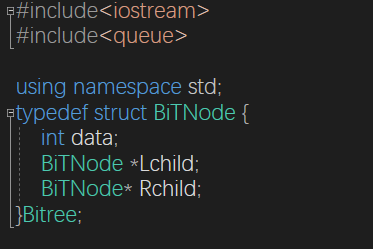
二叉树
- 度为2的树至少有3个节点,而二叉树可以为空
- 满二叉树高度为h,有2^h-1个节点,若父节点为i,左孩子为2*i,右节点为2*i-1
- 完全二叉树是满二叉树确实最下层最右边的一些连续的叶子节点,i
- 非空二叉树上的叶子节点数等于度为2的节点数+1,n0=n2+1
void initBiTree(BiTNode * &T) {
int curval; cin >> curval;
if (curval == -1)T = NULL;
else {
T = (BiTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
T->data = curval;
initBiTree(T->Lchild);
initBiTree(T->Rchild);
}
}
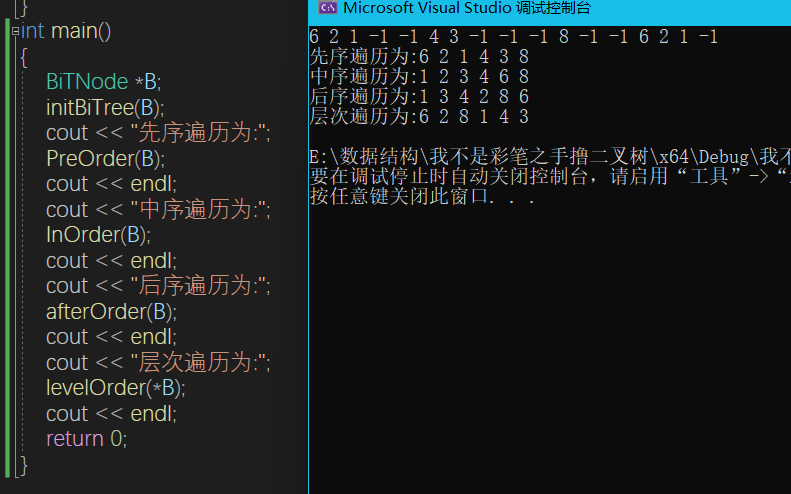
void PreOrder(Bitree *T) {
if (T != NULL) {
cout << T->data<<" ";
PreOrder(T->Lchild);
PreOrder(T->Rchild);
}
}
void InOrder(Bitree* T) {
if (T != NULL) {
InOrder(T->Lchild);
cout << T->data << " ";
InOrder(T->Rchild);
}
}
void afterOrder(Bitree* T) {
if (T != NULL) {
afterOrder(T->Lchild);
afterOrder(T->Rchild);
cout << T->data << " ";
}
}
void levelOrder(Bitree T) {
queue<BiTNode> q;
Bitree P;
q.push(T);
while (!q.empty()) {
P = q.front();
cout << P.data<<" ";
q.pop();
if (P.Lchild != NULL) {
q.push(*P.Lchild);
}
if (P.Rchild != NULL) {
q.push(*P.Rchild);
}
}
}树与二叉树的转换
森林和二叉树的转换
并查集
#include<iostream>
#define MAXN 10005
using namespace std;
int fa[MAXN];
void initUnion(int n);//并查集初始有n个节点
int find(int x);//查找x的祖先节点
void Union(int x, int y);//让x和y节点的祖先合并
void initUnion(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
fa[i] = i;
}
}
int find(int x) {
if (x == fa[x]) {
return x;
}
else
{
fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
return fa[x];
}
}
void Union(int x, int y) {
int fa_x = find(x);
int fa_y = find(y);
fa[fa_x] = fa_y;
}
//https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jv411a7LK?p=2
int main()
{
int m, n;
cin >> m >> n;
initUnion(m);
while (n--)
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
Union(x, y);
}
int Q;
cin >> Q;
while (Q--) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (fa[x] == y || fa[y] == x)cout << "yes";
else cout << "no";
}
return 0;
}图
BFS,DFS
BFS,DFS都可以进行图的无权遍历,但生成树不同
BFS
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
struct point {
int x;
int y;
point(int X = 0, int Y = 0) { x = X; y = Y; }
};
int dir[4][2] = { {0,1},{1,0},{-1,0},{0,-1} };
char mp[105][105];
int vis[105][105];
int startx, starty;
int endx, endy;
point que[105]; int front = 0, rear = 0;
int BFS(int x, int y) {
vis[x][y] = 1;
point *p = new point(x, y);
que[++rear] = *p;
while (rear != front) {
point temp = que[++front];
if (temp.x == endx && temp.y == endy) {
return vis[endx][endy]-1;
}
/*vis[temp.x][temp.y] += 1;*/
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newx = temp.x + dir[i][0];
int newy = temp.y + dir[i][1];
if ((mp[newx][newy] == '-'||mp[newx][newy]=='E') && vis[newx][newy] == 0) {
vis[newx][newy] = vis[temp.x][temp.y]+1;
point* curp = new point(newx, newy);
que[++rear] = *curp;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
memset(vis, 0,sizeof(vis)/sizeof(int));
front = rear = 0;
int m, n;
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin >> mp[i][j];
if (mp[i][j] == 'S') { startx = i; starty = j; }
if (mp[i][j] == 'E') { endx = i; endy = j; }
}
}
cout<<BFS(startx, starty);
}
return 0;
}DFS
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2] = { {0,1},{1,0},{-1,0},{0,-1} };
char mp[105][105];
int vis[105][105];
int startx, starty;
int endx, endy;
int flag = 0;
int ans[105]; int a = 0;
int an = 0;
void DFS(int x, int y) {
if (x == endx && y == endy) {
ans[a++] = an;
/*an = 0;*/
flag = 1; return;
}
/*if (flag == 1)return;*/
vis[x][y] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newx = x + dir[i][0];
int newy = y + dir[i][1];
if ((mp[newx][newy] == '-' || mp[newx][newy] == 'E') && vis[newx][newy] == 0)
{
vis[newx][newy] = 1;
an++;
DFS(newx, newy);
vis[newx][newy] = 0;
an--;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
int m, n;
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin >> mp[i][j];
if (mp[i][j] == 'S') { startx = i; starty = j; }
if (mp[i][j] == 'E') { endx = i; endy = j; }
}
}
DFS(startx, starty);
cout << *min_element(ans, ans + a);
}
return 0;
}详细见本博客前文章
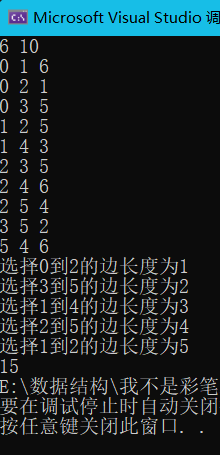
最小生成树(Kruskal算法)
prim算法从头节点开始找邻接最短边,然后依次寻找直到联通
这里我们主要学习Kruskal算法
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int from, to, dis;
}edge[1005];//描述一条边
int fa[1005];//并查集数组
void initUnion(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
fa[i] = i;
}
}
bool cmp(node &e1, node &e2) {
return e1.dis < e2.dis;
}
int find(int i) {
if (i == fa[i]) {
return i;
}
else {
fa[i] = find(fa[i]);
return find(fa[i]);
}
}
void unionn(int x, int y) {
int fa_x = find(x);
int fa_y = find(y);
fa[fa_x] = fa_y;
}
int main()
{
int n, m; cin >> n >> m;//n个顶点m条边
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> edge[i].from >> edge[i].to >> edge[i].dis;
}
initUnion(n);
sort(edge, edge + m, cmp);//排序途中所有的边找到最小的边
int k = 0;
int total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (k == n - 1)break;
if (find(edge[i].from) != find(edge[i].to)) {//只要选择的边不同根就选择这条较小边
unionn(edge[i].from, edge[i].to);
total += edge[i].dis;
k++;
}
}
cout << total;
return 0;
}最短单源路径算法
Dijkstra算法
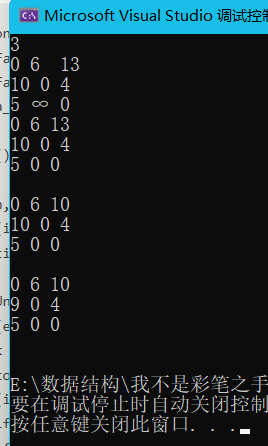
Floyd算法
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int mp[105][105];
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
cin>>mp[i][j];
if (mp[i][j] == -1)mp[i][j] = 99999;//表示无路径
}
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {//比较k次,每一次找到一个单源最短
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (mp[i][j] > mp[i][k] + mp[k][j]) {
mp[i][j] = mp[i][k] + mp[k][j];
}
cout << mp[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}查找
折半查找
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//折半查找
int half_search(int a[], int len,int x) {
int t = 0;
int low = 0; int high = len - 1, mid;
while (low <= high)
{
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (a[mid] == x) { cout << "折半查找共查找" << t << "次"<<endl; return mid; }
else if (a[mid] > x)high = mid - 1;
else {
low = mid + 1;
}
t++;
}
cout << "折半查找共查找" << t << "次";
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int a[5] = { 12,18,20,39,102 };
cout << half_search(a, 5, 102);
return 0;
}BST排序二叉树查找
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct Node {
int data;
Node* Lchild, * Rchild;
}*Bitree;
void createTree(Node* & T) {
T = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
int curval; cin >> curval;
if (curval == -1)
T = NULL;
else if (curval != -1) {
createTree(T->Lchild);
T->data = curval;
createTree(T->Rchild);
}
}
void preOrder(Bitree& T) {
if (T == NULL)
return;
cout << T->data << " ";
preOrder(T->Lchild);
preOrder(T->Rchild);
}
Node* BST_search(Bitree T, int key) {
while (T != NULL && T->data != key) {
if (key > T->data)T = T->Rchild;
else T = T->Lchild;
}
return T;
}
int BST_insert(Bitree& T, int num) {
if (T == NULL) {
T = (Bitree)malloc(sizeof(Node));
T->data = num;
T->Lchild = T->Rchild = NULL;
return 1;
}
else if (num == T->data)
return 0;
else if (num > T->data) {
return BST_insert(T->Rchild, num);
}
else {
return BST_insert(T->Lchild, num);
}
}
int main()
{
Bitree T;
createTree(T);
cout << BST_search(T, 2)->Lchild->data<<" "<< BST_search(T, 2)->Rchild->data<<endl;
BST_insert(T, 5);
preOrder(T);
return 0;
}如果是平衡二叉树时间复杂度为logn,如果直接线性排成一排则n
红黑树
蛮重要的,等会学
B树
最后一次更新于2022-02-21







0 条评论